What is the melting point of fluorine
Home » datasheet » What is the melting point of fluorineWhat is the melting point of fluorine
What Is The Melting Point Of Fluorine. C 4 H 6-322. This means that it will be solid at room temperature. Boiling point The temperature at which the liquidgas phase change occurs. The melting point of an element is basically the energy required to change the state of an element from its solid state to its liquid state.
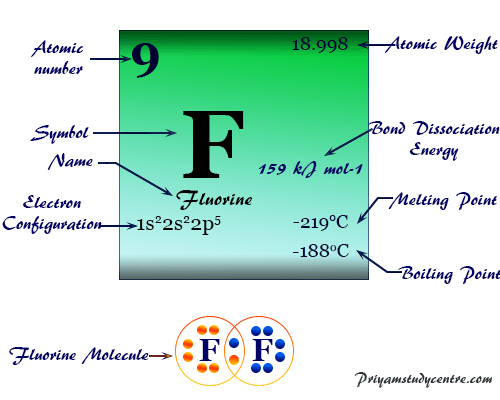 Fluorine Element Symbol Discovery Properties Uses Facts From priyamstudycentre.com
Fluorine Element Symbol Discovery Properties Uses Facts From priyamstudycentre.com
Alloy add-ons also suppress the melting range lower. C 3 H 6-1274. Energy of third ionisation. Are helium He neon Ne argon Ar krypton. Value given for hexagonal gray form. Another physical property that varies across a period is the melting point of the corresponding halide.
As the most electronegative element it is extremely reactive as it reacts with all other elements except for argon neon and helium.
The melting point is also referred to as liquefaction point solidus or liquidus. Value given for alpha form. Below the melting point the solid is the more stable state of the two. 137 ºC and B is benzoic acid mp. It is the lightest halogen and exists at standard conditions as a highly toxic pale yellow diatomic gas. Actual boiling point is 350C 1.
 Source: britannica.com
Source: britannica.com
Boiling point of Fluorine is -1881C. The chemical elements of the periodic chart sorted by. 21967C 36341F 5348 K Period 2 Boiling point. Iron is a chemical element in the periodic table that has the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. The boiling point of a substance is the temperature at which this phase change boiling.
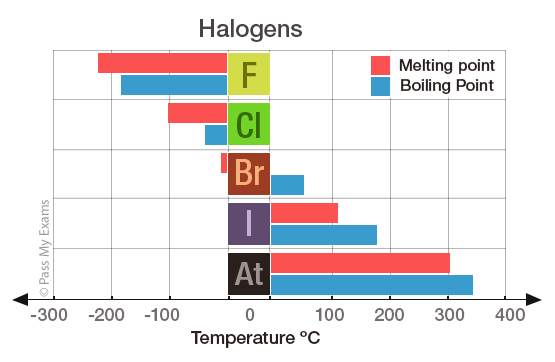 Source: passmyexams.co.uk
Source: passmyexams.co.uk
Iron Heavy Metal. For this reason fluorine does not occur free in nature and was extremely difficult for scientists to isolate. Energy of first ionisation. Hydrogen has a density of 008988 gL making it less dense than air. Minus 36332 degrees Fahrenheit minus 21962 degrees Celsius Boiling point.
 Source: material-properties.org
Source: material-properties.org
Fluorine is a pale yellow gas that reacts with most substancesThe free element melts at 220 C and boils at 188 CFinely divided metals burn in fluorine with a bright flameNineteen grams of fluorine will react with 10 gram of hydrogen. The halogens are five non-metallic elements found in group 17 of the periodic table. As the most electronegative element it is extremely reactive as it reacts with all other elements except for argon neon and helium. Value given for hexagonal gray form. Boiling point The temperature at which the liquidgas phase change occurs.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Why zinc has the lowest melting point in 3d metal series. Note that these points are associated with the standard atmospheric pressure. At the melting point the solid and liquid phases exist in equilibrium. 2-methylpropane isobutane CH 3 CHCH 3CH 3-1594. Iron is a chemical element in the periodic table that has the symbol Fe and atomic number 26.
 Source:
Source:
Fluorine is an univalent. At the melting point the two phases of a substance liquid and vapor have identical free energies and therefore are equally likely to exist. Helium does not solidify at standard pressure. Boiling point The temperature at which the liquidgas phase change occurs. C 4 H 6-322.
 Source: priyamstudycentre.com
Source: priyamstudycentre.com
Boiling points increases on moving down from fluorine to iodine. Note that these points are associated with the standard atmospheric pressure. 137 ºC and B is benzoic acid mp. Fluorine is a pale yellow gas that reacts with most substancesThe free element melts at 220 C and boils at 188 CFinely divided metals burn in fluorine with a bright flameNineteen grams of fluorine will react with 10 gram of hydrogen. Chemistry End of Chapter Exercises.
 Source: lizzyfluorine.weebly.com
Source: lizzyfluorine.weebly.com
Another physical property that varies across a period is the melting point of the corresponding halide. As the most electronegative element it is extremely reactive as it reacts with all other elements except for argon neon and helium. But melting and boiling points do not show regular trends. Click on any elements name for further chemical properties environmental data or health effects. Boiling points increases on moving down from fluorine to iodine.
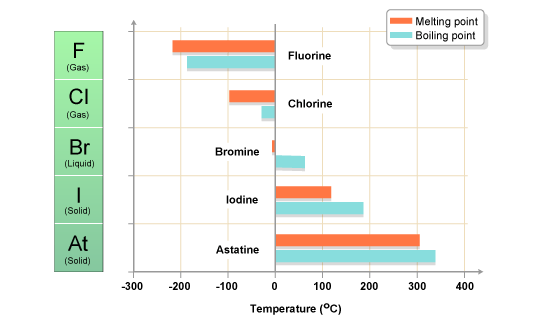 Source: daviddarling.info
Source: daviddarling.info
Reference Kelvin Celsius Fahrenheit Comments 1 H hydrogen H 2 use. In the following table the use row is the value recommended for use in other Wikipedia pages in order to maintain consistency across content. The melting point is also referred to as liquefaction point solidus or liquidus. Melting and boiling points of 3d metals. Up to date curated data provided by Mathematicas ElementData.
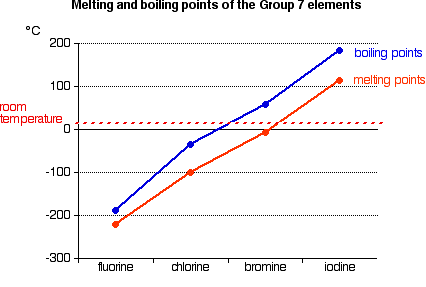 Source: chemguide.co.uk
Source: chemguide.co.uk
And the same is true for a sample of B containing a little A. Fluorines special status also stems from the fluorine factor the ability of this little atom to fine-tune the chemical properties of an entire molecule. Iron is a group 6 and period 4 metal. Fluorine is found in nature only in the form of its chemical compounds except for trace amounts of the free element in fluorspar that has been subjected to radiation from radiumNot a rare element it makes up about 0065 percent of Earths crust. 0136 nm -1.
 Source: rsc.org
Source: rsc.org
The melting point is also referred to as liquefaction point solidus or liquidus. The melting point of an element is basically the energy required to change the state of an element from its solid state to its liquid state. Thus higher the stronger the bond between the atoms higher will be the melting point. At normal atmospheric pressure carbon does not melt when heated it sublimes. As the most electronegative element it is extremely reactive as it reacts with all other elements except for argon neon and helium.
If you find this site convienient, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title what is the melting point of fluorine by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.