What is the melting point of caffeine
Home » datasheet » What is the melting point of caffeineWhat is the melting point of caffeine
What Is The Melting Point Of Caffeine. It is a molecular solid with low conductivity. Health Benefits of Caffeine Research indicates that caffeine may help protect human brain cells which lowers the risk of developing some diseases such as Parkinsons. Caffeine does not. -175 F -115 C 5 Flash Point.

Isomers are molecules that have different molecular structures but the same chemical formula. -175 F -115 C 5 Flash Point. Evaporated otherwise you may sublime the caffeine. Looking up the literature mp of caffeine prior to measuring the mp will give you an idea of the approximate temperature to be expected. Carefully observe the sample through the eyepiece and note down the temperature when. This is the diagonal line at stage I on the graph.
Caffeine has no stereoisomers as there are no tetrahedral structures with all different substituents preventing a chiral center See Figure 1.
25 F -4 C Vodka 40 alcohol by volume. It is the temperature at which the solid phase changes to the liquid phase. Measuring Melting point 1. Caffeine solution 10 mgmL in methanol ampule of 1 mL certified reference material. It is weakly basic pK a of conjugate acid 06 requiring strong acid to protonate it. Once a substance hits its melting point it is a.
25 F -4 C Vodka 40 alcohol by volume. The removal of caffeine from coffee beans with dichloromethane is an example of a solid liquid extraction. Melting Point of Caffeine. Crystal violet may be removed from a water solution by liquid-liquid extraction with n-amyl alcohol 1-pentanol. Other common applications of liquid-liquid extractions involve.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
29475 K Boiling point. 18030 Mean or Weighted MP VPmm Hg25 deg C. Carefully note your observations on what the sample looks like as it heats up. Do not exceed the 260oC limit of the thermometer. It is weakly basic pK a of conjugate acid 06 requiring strong acid to protonate it.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
The removal of caffeine from coffee beans with dichloromethane is an example of a solid liquid extraction. It is weakly basic pK a of conjugate acid 06 requiring strong acid to protonate it. It is used in research and development as well as in quality control in. Boiling Pt deg C. Removal of organic.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Pure anhydrous caffeine is a bitter-tasting white odorless powder with a melting point of 235238 C. The melting point of Caffeine is 238C. 1 Pa at 20 C Acidity pK a 774. -175 F -115 C 5 Flash Point. It is used in research and development as well as in quality control in.
 Source: sigmaaldrich.com
Source: sigmaaldrich.com
The snow can absorb energy all the way up until it hits its melting point of 32 degrees F. Boiling Point of Caffeine. Isomers are molecules that have different molecular structures but the same chemical formula. It is weakly basic pK a of conjugate acid 06 requiring strong acid to protonate it. 25 F -4 C Vodka 40 alcohol by volume.
 Source: lgcstandards.com
Source: lgcstandards.com
Place the capillary tube into the melting point apparatus and turn the heating stage on. Caffeine has an accurate melting point. Looking up the literature mp of caffeine prior to measuring the mp will give you an idea of the approximate temperature to be expected. Once a substance hits its melting point it is a. No natural isomers of caffeine exist.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
25 F -4 C Vodka 40 alcohol by volume. It is the temperature at which the solid phase changes to the liquid phase. Melting point mp analysis can also provide information about the purity of a sample. Melting point determination is the thermal analysis most frequently used to characterize solid crystalline materials. Isomers are molecules that have different molecular structures but the same chemical formula.
 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
Melting point is a characteristic property of solid crystalline substances. This is the diagonal line at stage I on the graph. The snow can absorb energy all the way up until it hits its melting point of 32 degrees F. A substance solid containing soluble impurities usually melts at a lower temperature than. It is odourless as there are no gas molecules being given off due to its solid state.

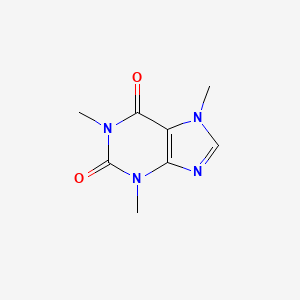
Caffeine is moderately soluble in water at room temperature 2 g100 mL but very soluble in boiling water 66 g100 mL. 238 deg C Subcooled liquid VP. Chemical Structure of Caffeine. Caffeine melting point standard United States Pharmacopeia USP Reference Standard. Caffeine is moderately soluble in water at room temperature 2 g100 mL but very soluble in boiling water 66 g100 mL.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Other common applications of liquid-liquid extractions involve. This is the diagonal line at stage I on the graph. Evaporated otherwise you may sublime the caffeine. Fill the vial to the shoulder with methanol cap the vial and shake to dissolve. It is odourless as there are no gas molecules being given off due to its solid state.
If you find this site serviceableness, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title what is the melting point of caffeine by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.