Stearic acid melting point
Home » datasheet » Stearic acid melting pointStearic acid melting point
Stearic Acid Melting Point. The generation of a novel intermediate of Zn 2 μ-O 2 CC 17 H 35 2 2 4X X. Melting Point of Stearic acid. Write the hydrogenation reaction for linoleic acid to hydrogenate all of the double bonds. If the melting point of the substance is below room temperature it will be a liquid - an oil.
 Melting Point Of Stearic Acid Download Scientific Diagram From researchgate.net
Melting Point Of Stearic Acid Download Scientific Diagram From researchgate.net
Good temperature 72 o F 22 o C Hydrogen Peroxide 10. Freely soluble in water. The trans-double bond isomer of oleic acid known as elaidic acid has a linear shape and a melting point of 45 ºC 32 ºC higher than its cis isomer. Answer sheet as MS Word or pdf. Palmitic acid stearic acid and oleic acid. The shapes of stearic and oleic acids are displayed in the models below.
Melting point is the temperature at which a given solid material changes from a solid state to a liquid or melts.
Melting point is the temperature at which a given solid material changes from a solid state to a liquid or melts. 1 Structures Expand this section. CH 3 CH 2 CO 2 H. Energy must be supplied to melt a solid. The exact composition strongly influences cocoa butters melting temperature and chocolate makers sometimes adjust the ratio of these fats in order to fine-tune that melting point. Good temperature 72 o F 22 o C Hydrocyanic Acid.
 Source: edu.rsc.org
Source: edu.rsc.org
The trans-double bond isomer of oleic acid known as elaidic acid has a linear shape and a melting point of 45 ºC 32 ºC higher than its cis isomer. The hydrogenation of a oleic fatty acid is shown in the graphic on the left. Maltitol is used as a coating agent. CID 5281 Stearic acid Component Compounds. C the physical properties of odor color and melting point within certain guidelines.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
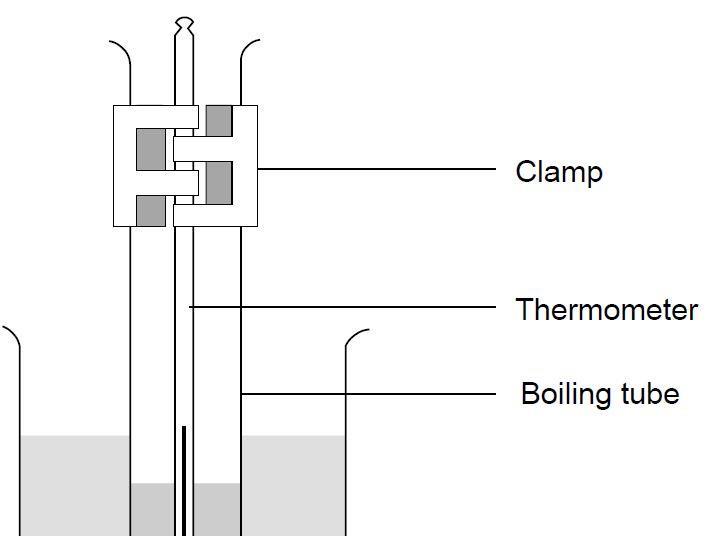
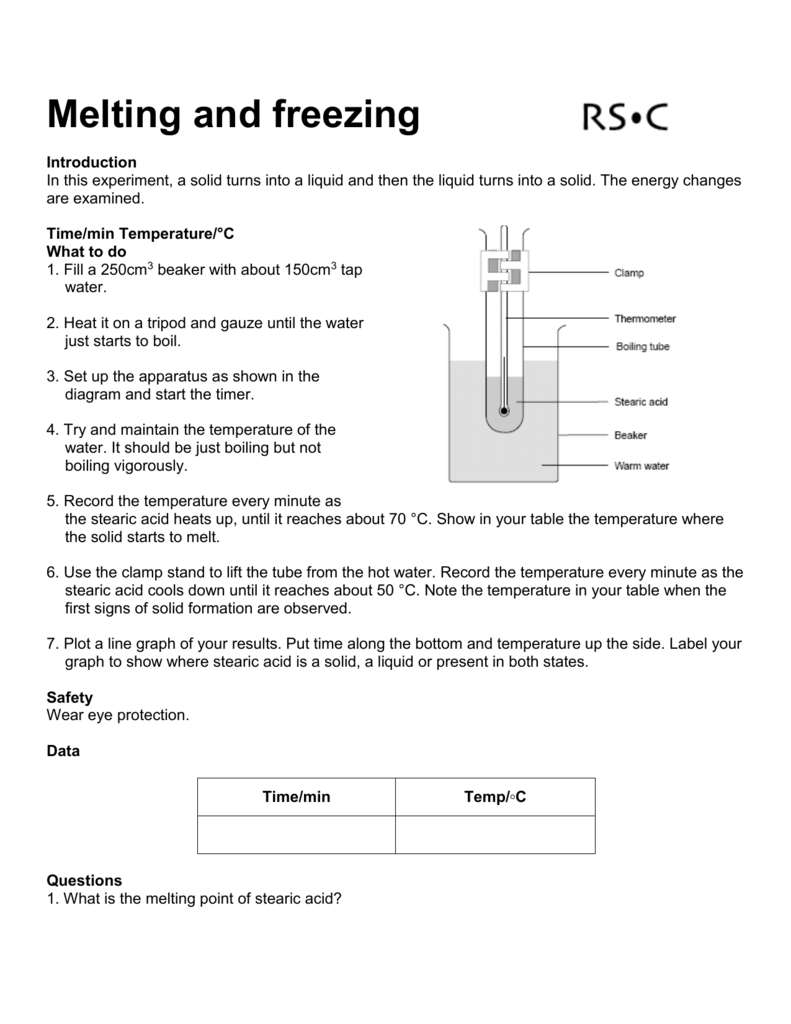
This presents a good opportunity to demonstrate how to maintain a steady temperature using a Bunsen burner. Boiling Point C Feature. For example the melting point of ice frozen water is 0 C. The melting point of a substance is the temperature at which it changes state from solid to liquid at atmospheric pressure. Maltitol is used as a coating agent.
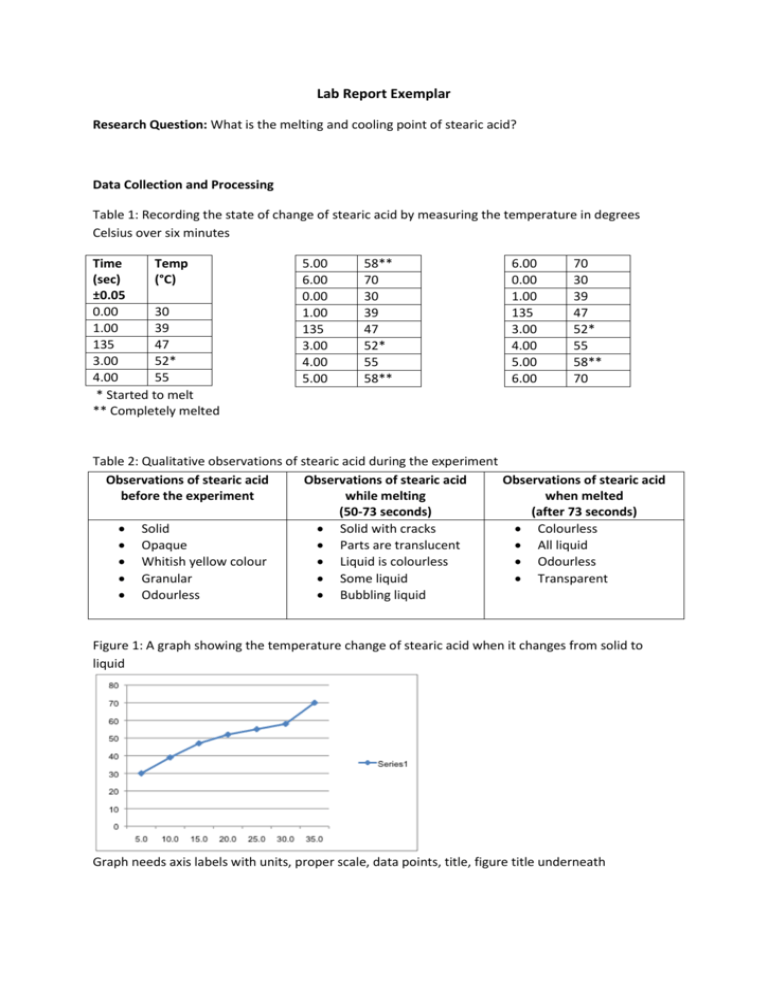 Source: studylib.net
Source: studylib.net
If the melting point of the substance is below room temperature it will be a liquid - an oil. This is discussed in detail on another page. Melting point is the temperature at which a given solid material changes from a solid state to a liquid or melts. Saturated and unsaturated fats omega-3 and omega-6 fats trans fats even the melting points of fats. 95 500µm 40 100µm in size for Maltisorb P200 Roquette.
 Source: tes.com
Source: tes.com
Three fatty acids plus a glycerol molecule snap. Freely soluble in water. E the physical property of solubility in nonpolar organic solvents. The melting point is the highest temperature at which crystallization may occur. This presents a good opportunity to demonstrate how to maintain a steady temperature using a Bunsen burner.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
These are all determined by where and how many of those double bonds there are. CH 3 CH 2 3 CO 2 H. We say that such a body melts. This observed in the series lauric C12 palmitic C16 stearic C18. Palmitic acid or hexadecanoic acid in IUPAC nomenclature is the most common saturated fatty acid found in animals plants and microorganisms.
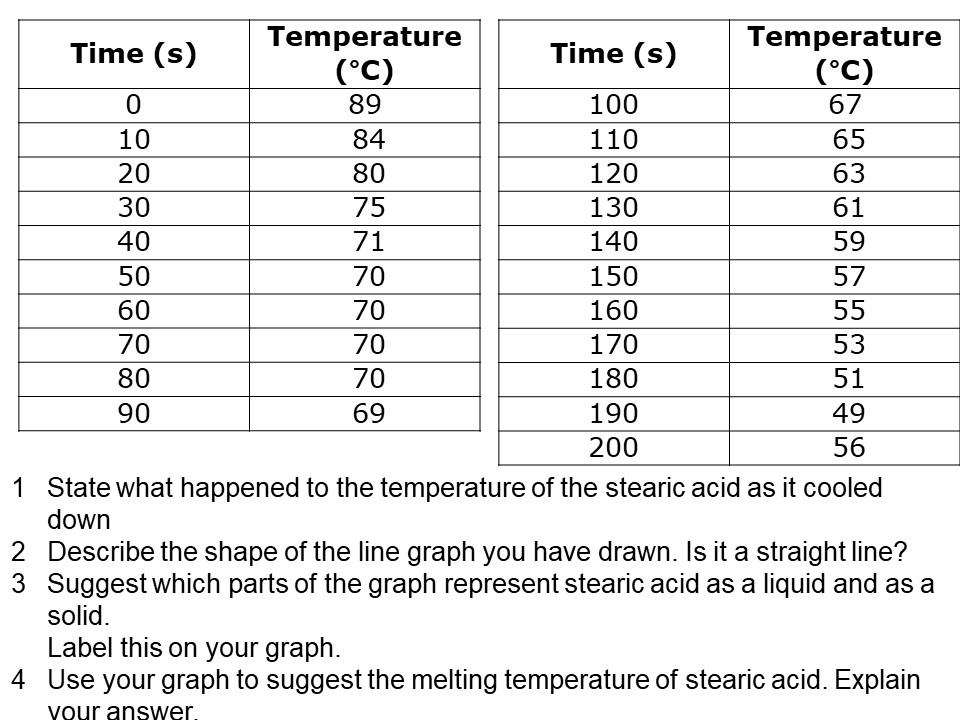 Source: tes.com
Source: tes.com
The generation of a novel intermediate of Zn 2 μ-O 2 CC 17 H 35 2 2 4X X. CH 3 CH 2 CO 2 H. Fenghe Qiu in Accelerated Predictive Stability 2018. CID 5462224 Magnesium CID 5281 Stearic acid Dates. The lower melting point of oils is related to the higher degree of unsaturation.
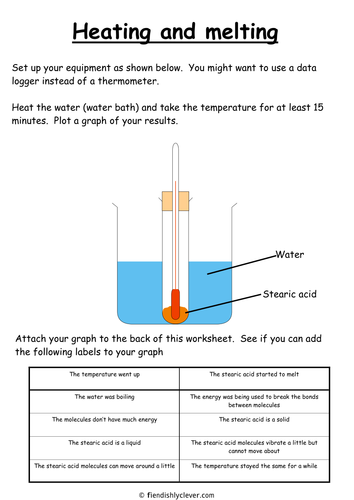
Remind students not to attempt to move the thermometer in the solid stearic acid as it will break. This fatty acid has profound and diverse effects on liver metabolism. As the molecular weight increases the melting point increases. Butyrum butanoic acid-55 ºC. Two polyunsaturated fatty acids linoleic and linolenic are.
 Source: rogerfrost.com
Source: rogerfrost.com
A substances melting point depends on pressure and is usually specified at standard pressure in reference materials. Good temperature 72 o F 22 o C Hydrocyanic Acid. Melting Point C Physical Form. It is also a temperature at which a solid crystal turns into a liquid. The presence of carbon to carbon double bonds in the oil molecules distorts the long fatty acid chains and the.
 Source: studylib.net
Source: studylib.net
Vegetable oils are. Two polyunsaturated fatty acids linoleic and linolenic are. It is also a temperature at which a solid crystal turns into a liquid. In this case oleic acid would become stearic acid These double bonds are the secret to understanding fat. If the melting point is above room temperature it will be a solid - a fat.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
This observed in the series lauric C12 palmitic C16 stearic C18. The hydrogenation of a oleic fatty acid is shown in the graphic on the left. Saturated and unsaturated fats omega-3 and omega-6 fats trans fats even the melting points of fats. It is used in. The melting point is also referred to as liquefaction point solidus or liquidus.
If you find this site beneficial, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title stearic acid melting point by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.