Potassium chloride melting point
Home » datasheet » Potassium chloride melting pointPotassium chloride melting point
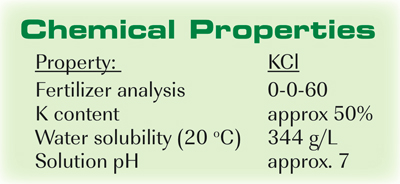
Potassium Chloride Melting Point. The melting point of a substance is the temperature at which it changes state from solid to liquid at atmospheric pressure. Lithium melts at 1805 C 3569 F. The melting point is the highest temperature at which crystallization may occur. The melting point is also referred to as liquefaction point solidus or liquidus.
 Potassium Chloride Mosaic Crop Nutrition From cropnutrition.com
Potassium Chloride Mosaic Crop Nutrition From cropnutrition.com
The melting point is also referred to as liquefaction point solidus or liquidus. It is also a temperature at which a solid crystal turns into a liquid. Melting point - the temperature at which a solid turns into a liquid. Potassium chloride is mainly useful in making fertilizers since plants need potassium for their growth and development. The name is derived from the english word potash. Energy of first ionisation.
A substances melting point depends on pressure and is usually specified at standard pressure in reference materials.
Potash can be used to make glass and soap etc. Melting Point and Boiling point- Melting point is a characteristic property of solid crystalline substances. The melting point of a substance is the temperature at which it changes state from solid to liquid at atmospheric pressure. The melting point is also referred to as liquefaction point solidus or liquidus. With such a high melting point pipes containing sodium must be heated electrically and thermally insulated to prevent freezing. This is also useful in.
 Source: pediaa.com
Source: pediaa.com
Therefore it readily releases potassium into soil water so that plants can take in potassium easily. Potassium chloride is mainly useful in making fertilizers since plants need potassium for their growth and development. It is soft and shiny metal which has a melting point 63 degrees and the boiling point as 770 degrees. Below the melting point the solid is the more stable state of the two. We say that such a body melts.

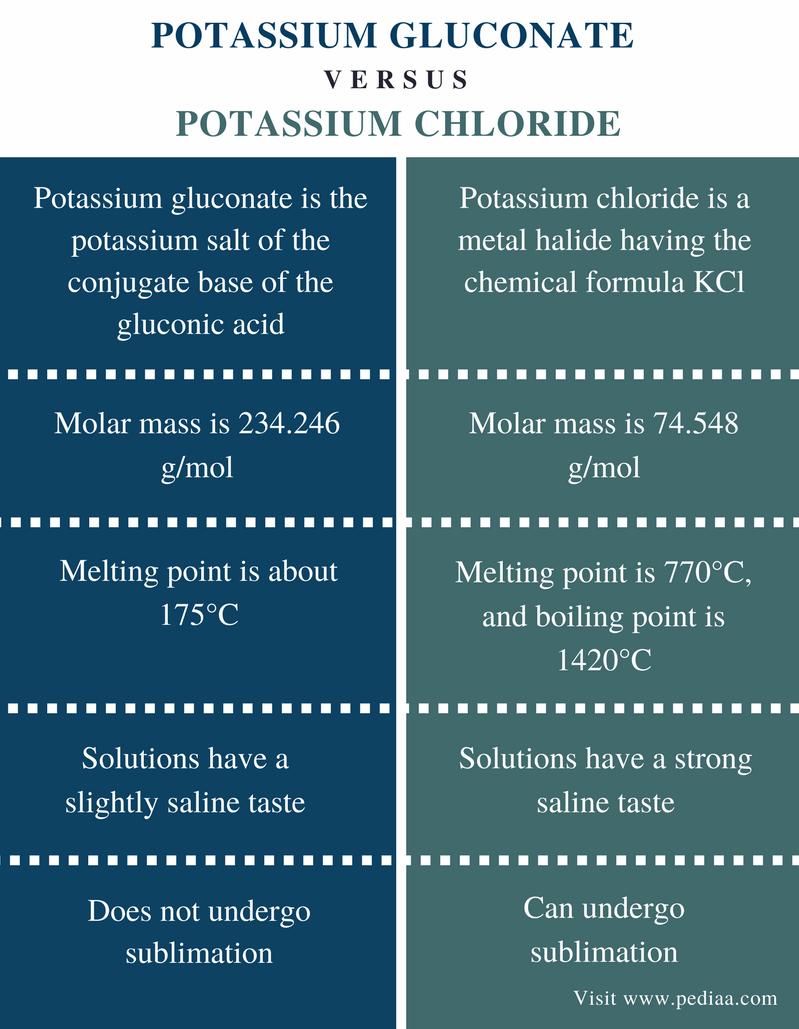
Its melting point is about 770 C and the boiling point is 1420 C. The solid dissolves readily in water and its solutions have a salt-like tastePotassium chloride can be obtained from ancient dried lake deposits. The chemical symbol K comes from kalium the Mediaeval Latin for potash which may have derived from the. At the melting point the two phases of a substance liquid and vapor have identical free energies and therefore are equally likely to exist. Physical and Chemical Properties Of Potassium.
 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
Potassium chlorate is a compound containing potassium chlorine and oxygen with the molecular formula KClO 3In its pure form it is a white crystalline substance. This agent has potential antihypertensive effects and when taken as a nutritional. Cesium melts at just 284 C 831 F. KCl being a salt is highly soluble in water. Potassium chloride KCl or potassium salt is a metal halide salt composed of potassium and chlorineIt is odorless and has a white or colorless vitreous crystal appearance.
 Source: cropnutrition.com
Source: cropnutrition.com
Potassium chlorate and sulfuric acid react to cause fire and possible explosions Mellor 2315. Substance Formula Melting point C Boiling temperature C Density 25C. We say that such a body melts. The solid dissolves readily in water and its solutions have a salt-like tastePotassium chloride can be obtained from ancient dried lake deposits. A solution is saturated if it wont dissolve any more of the salt at that particular temperature - in the presence of crystals of.
 Source: ddbst.com
Source: ddbst.com
In other applications it is mostly obsolete and has been. Adding a heat will convert the solid into a liquid with no temperature change. This is also useful in. A solubility curve shows how the solubility of a salt like sodium chloride or potassium nitrate varies with temperature. Furthermore all of these compounds have low boiling points typically in the range of 50 C to.
 Source: crystran.co.uk
Source: crystran.co.uk
A solubility curve shows how the solubility of a salt like sodium chloride or potassium nitrate varies with temperature. Alternatively a sodium-potassium NaK alloy which is a liquid at ambient temperatures for potassium compositions between 46 and 89 wo can be employed. A substances melting point depends on pressure and is usually specified at standard pressure in reference materials. For example the melting point of sodium chloride NaCl is 808 C. Lithium melts at 1805 C 3569 F.
 Source: chemicalbook.com
Source: chemicalbook.com
Its melting point is about 770 C and the boiling point is 1420 C. After sodium chlorate it is the second most common chlorate in industrial use. This is also useful in. The solubility is often although not always measured as the mass of salt which would saturate 100 grams of water at a particular temperature. At the melting point the two phases of a substance liquid and vapor have identical free energies and therefore are equally likely to exist.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
It is the temperature at which the solid phase changes to the liquid phaseThis is the point at which both liquid and solid phases exist at equilibriumVisit BYJUS to learn more about the Principle Detailed Explanation Videos and FAQs of melting point and Boiling point. Potash can be used to make glass and soap etc. The melting point is the highest temperature at which crystallization may occur. At the melting point the two phases of a substance liquid and vapor have identical free energies and therefore are equally likely to exist. In other applications it is mostly obsolete and has been.
 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
The melting point also defines a condition in which the solid and liquid can exist in equilibrium. Potassium chlorate is a compound containing potassium chlorine and oxygen with the molecular formula KClO 3In its pure form it is a white crystalline substance. Melting point - the temperature at which a solid turns into a liquid. For full table with Density Liquid Denity at Melting Point and Water Solubility-rotate the screen. The alkali metals have low melting points.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
In contrast the melting points of the non-metal halides from Periods 2 and 3 such as CCl 4 PCl 3 and SCl 2 are below 0 C so these materials are liquids at room temperature. The alkali metals are very reactive and so are usually found in compounds with other elements such as salt sodium chloride NaCl and potassium. Potassium chloride KCl or potassium salt is a metal halide salt composed of potassium and chlorineIt is odorless and has a white or colorless vitreous crystal appearance. For example the melting point of sodium chloride NaCl is 808 C. Alternatively a sodium-potassium NaK alloy which is a liquid at ambient temperatures for potassium compositions between 46 and 89 wo can be employed.
If you find this site good, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title potassium chloride melting point by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.