Melting point of magnesium oxide
Home » datasheet » Melting point of magnesium oxideMelting point of magnesium oxide
Melting Point Of Magnesium Oxide. Magnesium Melting Point and Boiling Point. At the melting point the two phases of a substance liquid and vapor have identical free energies and therefore are equally likely to exist. Melting point - the temperature at which a solid turns into a liquid. Magnesium alloy car engine blocks.
 C2 Why Is The Melting Point Of Mgo Higher Than Nacl Youtube From youtube.com
C2 Why Is The Melting Point Of Mgo Higher Than Nacl Youtube From youtube.com
Magnesium is a Group 2 alkaline earth element within the periodic table and has a relative atomic mass of 24305 Da a specific gravity at 20C of 1738 2 3 a melting point of 6488C and a boiling point of 1090C. Some of its other uses include spark plug insulators micro-electric substrates and insulating heatsinks 1. About 20 is used in castings and wrought products. In general boiling is a phase change of a substance from the liquid to the gas phase. It is a white solid used in the manufacture of high-temperature refractory bricks electrical and thermal insulators cements fertilizer. The addition of magnesium to aluminium produces high-strength corrosion-resistant alloys.
Why does Magnesium Oxide have a higher melting point than Sodium Chloride.
Alumina films are also vital components in the microchip industry. These ionic bonds are strong and require a large amount of thermal energy to overcome them and break the structure enabling it to change state from a solid. Alumina films are also vital components in the microchip industry. Magnesium alloy car engine blocks. It contains equivalent of 68-80 of magnesium oxide 4030. Vulcanization is a chemical process in which the rubber is heated with sulphur accelerator and activator at 140160C.
 Source: chemistry.stackexchange.com
Source: chemistry.stackexchange.com
Both Magnesium Oxide and Sodium Chloride exist as a giant ionic lattices where each oppositely charged ion is held in place by a strong electrostatic attractions. Magnesium chloride is the name for the chemical compound with the formula MgCl 2 and its various hydrates MgCl 2 H 2 O xAnhydrous MgCl 2 contains 255 elemental magnesium by mass. These salts are typical ionic halides being highly soluble in waterThe hydrated magnesium chloride can be extracted from brine or sea waterIn North America magnesium chloride is produced primarily from Great. Melting point is the temperature at which a solid turns into a liquid. The melting point is specific for a given substanceFor example the melting point of ice frozen water is 0 C.
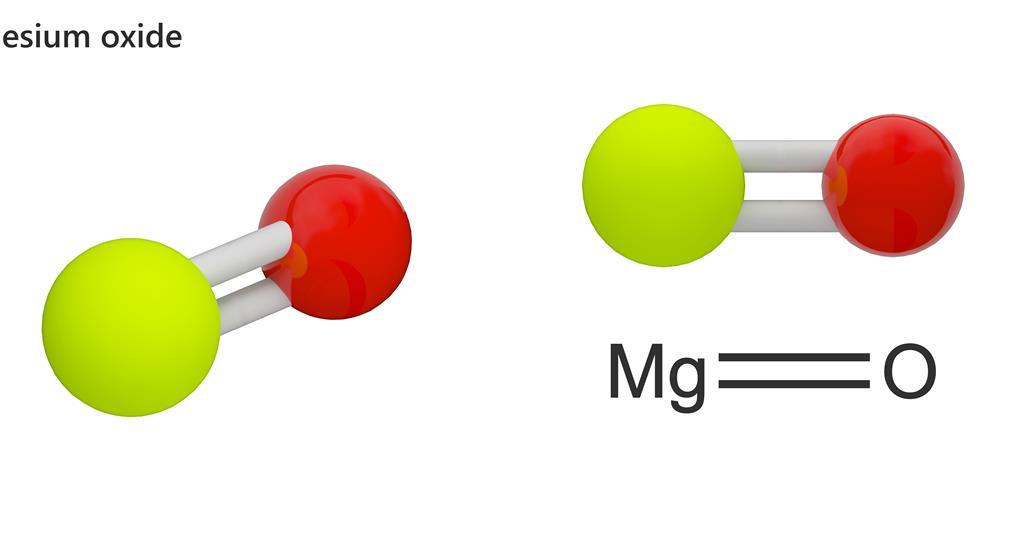 Source: chemistryworld.com
Source: chemistryworld.com
Note that these points are associated with the standard atmospheric pressure. These ionic bonds are strong and require a large amount of thermal energy to overcome them and break the structure enabling it to change state from a solid. The largest single use for magnesium metal is in aluminium alloying accounting for about 50 of the total magnesium metal consumption. Substance Formula Melting point C Boiling temperature C Density 25C. Melting point of Magnesium is 649C.
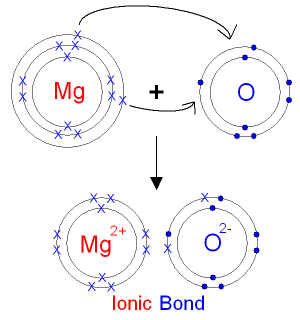 Source: gcsescience.com
Source: gcsescience.com
Water freezes at the same temperature and turns into ice. Magnesium Melting Point and Boiling Point. Magnesium stearate is compd of magnesium with mixture of solid org acids obtained from fats consists chiefly of variable proportions of magnesium stearate magnesium palmitate. When fine particles of magnesium oxide are dispersed in air whether directly or when generated by the burning or cutting of magnesium metal the resulting magnesium oxide fume is an inhalation hazard. It contains equivalent of 68-80 of magnesium oxide 4030.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Vulcanization is a chemical process in which the rubber is heated with sulphur accelerator and activator at 140160C. When fine particles of magnesium oxide are dispersed in air whether directly or when generated by the burning or cutting of magnesium metal the resulting magnesium oxide fume is an inhalation hazard. The melting point is the highest temperature at which crystallization may occur. Melting point is the temperature at which a solid turns into a liquid. Magnesium Melting Point and Boiling Point.
 Source: crystran.co.uk
Source: crystran.co.uk
Melting point of Magnesium is 649C. Melting point - the temperature at which a solid turns into a liquid. The process involves the formation of cross-links between long rubber molecules so as to achieve improved elasticity resilience tensile strength viscosity hardness and weather resistance. The dicalcium silicate slag produced by the above processes has a melting point of about 2000 C 3600 F and is therefore present as a solid but by adding alumina aluminum oxide Al 2 O 3 to the charge the melting point can be reduced to 15501600 C 28252900 F. The thermal and electrical conductivity of magnesium and its melting point are very similar to those of aluminum.
 Source: docbrown.info
Source: docbrown.info
When fine particles of magnesium oxide are dispersed in air whether directly or when generated by the burning or cutting of magnesium metal the resulting magnesium oxide fume is an inhalation hazard. Why does Magnesium Oxide have a higher melting point than Sodium Chloride. Magnesium alloy car engine blocks. See Standard state and enthalpy of formation Gibbs free energy of formation entropy and heat capacity for thermodynamic data for the same compounds. Alumina films are also vital components in the microchip industry.
 Source: britannica.com
Source: britannica.com
For example ice is a solid form of water that melts at 0 degrees Celsius32 degrees Fahrenheit and changes to its liquid form. In theory the melting point of a solid is the same as the freezing point of the liquid the point at which it turns into a solid. Covalent bonds in which the sharing of the electron pair is unequal with the electrons spending more time around the more nonmetallic atom are called polar covalent bonds. The thermal and electrical conductivity of magnesium and its melting point are very similar to those of aluminum. In general boiling is a phase change of a substance from the liquid to the gas phase.
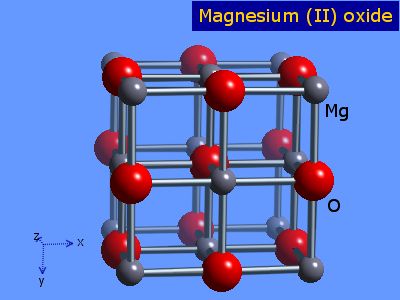 Source: webelements.com
Source: webelements.com
The thermal and electrical conductivity of magnesium and its melting point are very similar to those of aluminum. Note that these points are associated with the standard atmospheric pressure. In such a bond there is a charge separation with one atom being slightly more positive and the other more negative ie the bond will produce a dipole moment. The melting point is specific for a given substanceFor example the melting point of ice frozen water is 0 C. When fine particles of magnesium oxide are dispersed in air whether directly or when generated by the burning or cutting of magnesium metal the resulting magnesium oxide fume is an inhalation hazard.
 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
With a melting point of 2700ºC and a thermal expansion coefficient of 10810-5 K-1 zirconium dioxide is widely known for its high resistance to heat. See Standard state and enthalpy of formation Gibbs free energy of formation entropy and heat capacity for thermodynamic data for the same compounds. Melting point is the temperature at which a solid turns into a liquid. For full table with Density Liquid Denity at Melting Point and Water Solubility-rotate the screen. Some of its other uses include spark plug insulators micro-electric substrates and insulating heatsinks 1.
 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
Its high melting and boiling points in addition to its excellent thermal resistive properties make aluminium oxide desirable in the manufacture of high-temperature furnace insulations and electrical insulators. Both Magnesium Oxide and Sodium Chloride exist as a giant ionic lattices where each oppositely charged ion is held in place by a strong electrostatic attractions. In such a bond there is a charge separation with one atom being slightly more positive and the other more negative ie the bond will produce a dipole moment. Once ignited magnesium metal burns in air with a characteristic blinding bright white flame to give a mixture of white magnesium oxide MgO and magnesium nitride Mg 3 N 2. These ionic bonds are strong and require a large amount of thermal energy to overcome them and break the structure enabling it to change state from a solid.
If you find this site good, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title melting point of magnesium oxide by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.