Melting point of fluorine
Home » datasheet » Melting point of fluorineMelting point of fluorine
Melting Point Of Fluorine. This means that it will be solid at room temperature. Value given for diamond form. Fluorine is found in nature only in the form of its chemical compounds except for trace amounts of the free element in fluorspar that has been subjected to radiation from radiumNot a rare element it makes up about 0065 percent of Earths crust. The halogens are five non-metallic elements found in group 17 of the periodic table.
 Fluorine Thermal Properties Melting Point Thermal Conductivity Expansion From material-properties.org
Fluorine Thermal Properties Melting Point Thermal Conductivity Expansion From material-properties.org
At the melting point the solid and liquid phases exist in equilibrium. 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6. Minus 30662 degrees F minus 18812 degrees C Number of. 24867 C 4155 F boiling point. Learn More in these related Britannica articles. Click on any elements name for further chemical properties environmental data or health effects.
At the melting point the two phases of a substance liquid and vapor have identical free energies and therefore are equally likely to exist.
Let us look at the elements in the ascending order of their melting points. C 3 H 4-1027. It has two distinct oxidation states 1 -1 which make it able to act as both an oxidizing and a reducing agent. The term halogen means salt-former and compounds containing halogens are called salts. Chemistry End of Chapter Exercises. 137 ºC and B is benzoic acid mp.
 Source: britannica.com
Source: britannica.com
Iron is a chemical element in the periodic table that has the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. Boiling point The temperature at which the liquidgas phase change occurs. Actual boiling point is 350C 1. As the most electronegative element it is extremely reactive as it reacts with all other elements except for argon neon and helium. Atomic number - Name alphabetically-272.
 Source: sites.google.com
Source: sites.google.com
21967C 36341F 5348 K Period 2 Boiling point. The principal fluorine-containing minerals are 1 fluorspar deposits of which occur in Illinois Kentucky Derbyshire southern Germany the. Melting Points of the Halides. The term halogen means salt-former and compounds containing halogens are called salts. 2-methylpropane isobutane CH 3 CHCH 3CH 3-1594.
 Source: chemguide.co.uk
Source: chemguide.co.uk
Atomic number - Name alphabetically-272. Melting and boiling points of 3d metals are generally higher than s block elements. Standard potential - 287 V. Chemistry End of Chapter Exercises. Atomic number - Name alphabetically-272.
 Source: rsc.org
Source: rsc.org
Value given for monoclinic beta form. Minus 36332 degrees Fahrenheit minus 21962 degrees Celsius Boiling point. It is the lightest halogen and exists at standard conditions as a highly toxic pale yellow diatomic gas. Thus higher the stronger the bond between the atoms higher will be the melting point. Actual boiling point is 350C 1.
 Source: lizzyfluorine.weebly.com
Source: lizzyfluorine.weebly.com
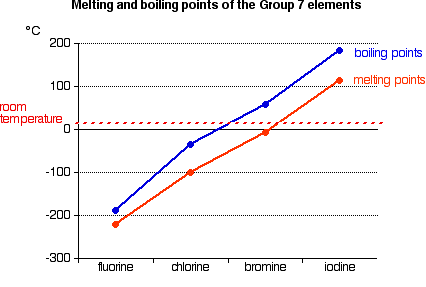
Energy of third ionisation. Classify the six underlined properties in the following paragraph as chemical or physical. Another physical property that varies across a period is the melting point of the corresponding halide. Melting point of Fluorine is -2198C. Sublimation The transition of a substance directly from the solid to the gas phase without passing through a liquid phase.
 Source: passmyexams.co.uk
Source: passmyexams.co.uk
Alloy add-ons also suppress the melting range lower. As the most electronegative element it is extremely reactive as it reacts with all other elements except for argon neon and helium. Click on any elements name for further chemical properties environmental data or health effects. For this reason fluorine does not occur free in nature and was extremely difficult for scientists to isolate. Boiling point The temperature at which the liquidgas phase change occurs.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
At normal atmospheric pressure arsenic does not melt when heated. Hydrogen has a melting point of -25914 C and a boiling point of -25287 C. 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6. The term halogen means salt-former and compounds containing halogens are called salts. 137 ºC and B is benzoic acid mp.
 Source: elevise.co.uk
Source: elevise.co.uk
C 4 H 8-1055. Minus 36332 degrees Fahrenheit minus 21962 degrees Celsius Boiling point. The term halogen means salt-former and compounds containing halogens are called salts. Energy of first ionisation. The melting point of a substance is the temperature at which it changes state from solid to liquid at atmospheric pressure.
 Source: material-properties.org
Source: material-properties.org
In the following table the use row is the value recommended for use in other Wikipedia pages in order to maintain consistency across content. Boiling point The temperature at which the liquidgas phase change occurs. Are helium He neon Ne argon Ar krypton. If the pressure is increased to 10 atmospheres carbon graphite is observed to melt at 3550 C. Alloy add-ons also suppress the melting range lower.
 Source: chemguide.co.uk
Source: chemguide.co.uk
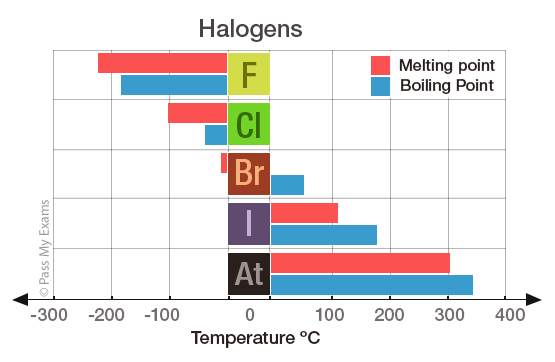
Fluorine is a chemical element with the symbol F and atomic number 9. The melting point of a substance is the temperature at which it changes state from solid to liquid at atmospheric pressure. 2 - Atomic number-259. Hydrogen exists in two different spin isomers of hydrogen diatomic molecules that differ by the. Melting Points of the Halides.
If you find this site adventageous, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title melting point of fluorine by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.