Melting point of dichloromethane
Home » datasheet » Melting point of dichloromethaneMelting point of dichloromethane
Melting Point Of Dichloromethane. 967 C 1421 F. 3128 K decomposes at 720 C 3975 C 10355 F. ILO International Chemical Safety Cards. 5561 C 10330 F Explosion limits.
The solution of these dissolved compounds is referred to as the extract. It is also a temperature at which a solid crystal turns into a liquid. The melting point of benzoic acid is approximately 122 C 2002 Gilbert and Martin CD-Rom MSDS Data. 1765 K Boiling point. Melting PointRange-97 C -1426 F Boiling PointRange 39 C 1022 F Flash Point No information available Evaporation Rate No information available Flammability solidgas Not applicable Flammability or explosive limits Upper 23 vol Lower 13 vol Vapor Pressure 350 mbar. ILO International Chemical Safety Cards.
In selecting a solvent consider that like likes like.
967 C 1421 F. New Window-2173 F NTP 1992 National Toxicology Program Institute of Environmental Health Sciences National Institutes of Health NTP. The melting point of Caffeine is 238C. 189 and 286 D for dichloromethane and trifluorotoluene respectively. 398-40C 1036-104F Flash Point. Point below the melting point of the compound being purified because solid melts before dissolves oiling out.
 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
Dichloromethane was separated out during the ethanol boiling stage due to its low boiling point 403. News See more News Events. Point below the melting point of the compound being purified because solid melts before dissolves oiling out. 398-40C 1036-104F Flash Point. Research Triangle Park North Carolina.
 Source: acs.org
Source: acs.org
Dichloromethane is a member of the class of chloromethanes that is methane in which two of the hydrogens have been replaced by chlorineA dense non-flammible colourless liquid at room temperature bp. Extraction is a method used for the separation of organic compound from a mixture of compound. Point below the melting point of the compound being purified because solid melts before dissolves oiling out. The melting point is the highest temperature at which crystallization may occur. A drying procedure is therefore necessary to remove all traces of water before the solvent is evaporated.

A drying procedure is therefore necessary to remove all traces of water before the solvent is evaporated. In selecting a good recrystallization solvent one should also consider flammability toxicity and expense. Next time weight the crystals of caffeine and determine their melting point. Dichloromethane was separated out during the ethanol boiling stage due to its low boiling point 403. 12 Vol Upper.
Source: merckmillipore.com
97C 207F Boiling Point. For example the melting point of ice frozen water is 0 C. Carefully note your observations on what the sample looks like as it heats up. If the solvent were evaporated at this point the resulting solid neutral compound would be wet with water and would consequently be a gooey mess and would take a long time to dry. BDH-120 Page 1 of 9 1.
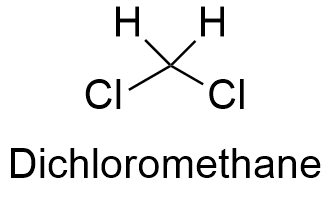 Source: softschools.com
Source: softschools.com
Melting point of DCM-976 0 C. Solvent formula polarity boiling point 0 C water H2O very polar 100 ethanol CH3CH2OH polar 78 methanol CH3OH polar 65 dichloromethane CH2Cl2 slightly polar 40 diethyl ether CH3CH22O slightly polar 35 Organic compounds with one polar functional group and a low number of carbon atoms such. In the case of Caffeine extraction from tea powder the solubility of caffeine in water. Ethyl acetate CH 3 COOC 2 H 5 is an excellent solvent with boiling point 78 C 172 F. Carefully note your observations on what the sample looks like as it heats up.
 Source: fishersci.co.uk
Source: fishersci.co.uk
967 C 1421 F. Dichloromethane methylene chloride CH 2 Cl 2 is useful as a solvent pair with ligroin but its boiling point 35 C 95 F is too low to make it a good crystallization solvent. The most commonly used recrystallization solvents are presented in the following table. Since most of the extractions are performed using aqueous solutions ie 5 NaOH 5 HCl the miscibility of the solvent with water is a crucial point as well as the compatibility of the reagent with the compounds and the solvent of the solution to be extracted. The melting point is the highest temperature at which crystallization may occur.
 Source: sciencemadness.org
Source: sciencemadness.org
350 mm Hg at 68F 20C VAPOUR DENSITY air 10. The presence of a soluble impurity almost always causes a decrease in the melting point expected for the pure compound and a broadening of the. -4C 25 F s Ignition temperature. Dichloromethane methylene chloride CH 2 Cl 2 is useful as a solvent pair with ligroin but its boiling point 35 C 95 F is too low to make it a good crystallization solvent. 256 gL 15 C 175 gL 25 C 158 gL 30 C 52 gL 60 C Solubility.
Source: chemspider.com
Do not exceed the 260oC limit of the thermometer. The melting point depends on the pressure. The melting point of benzoic acid is approximately 122 C 2002 Gilbert and Martin CD-Rom MSDS Data. Polar compounds dissolve polar compounds and non-polar compounds dissolve non-polar compounds. The melting point range is defined as the span of temperature from the point at which the crystals first begin to liquefy to the point at which the entire sample is liquid.
 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
Next time weight the crystals of caffeine and determine their melting point. A drying procedure is therefore necessary to remove all traces of water before the solvent is evaporated. The solution of these dissolved compounds is referred to as the extract. Gilbert and Martin Experimental. It is also used as a degreasing agent.
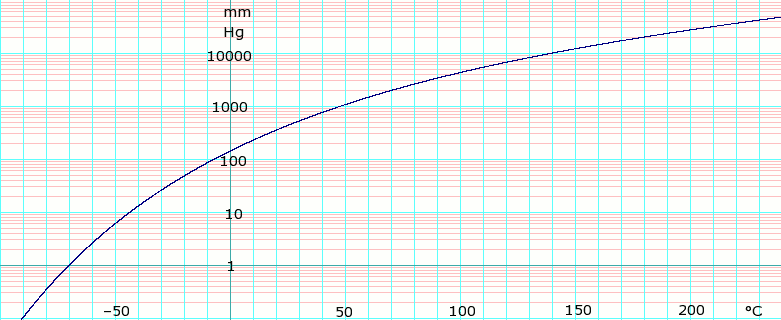 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
Distinct solvent-like odour TGAI weak not characteristic pure AI Melting point. As the compound is highly volatile in nature it can cause acute inhalation hazards. 97C 207F Boiling Point. The presence of a soluble impurity almost always causes a decrease in the melting point expected for the pure compound and a broadening of the. BUCHIs melting point analyzers fully automate the rather time-consuming process of melting point and boiling point determination and provide highly accurate results.
If you find this site helpful, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title melting point of dichloromethane by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.