Melting point of boron
Home » datasheet » Melting point of boronMelting point of boron
Melting Point Of Boron. They are equidistantly separated with respect to the main resistance peak. Boron tribromide appears as a colorless fuming liquid with a pungent odor. I dont know anyone who thinks the element boron has anything interesting about it. A substances melting point depends on pressure and is usually specified at standard pressure in reference materials.
 Boron Element Information Properties And Uses Periodic Table From rsc.org
Boron Element Information Properties And Uses Periodic Table From rsc.org
At room temperature it. Value given for diamond form. Boron has also been used in some rockets as an ignition source. Boiling point of Boron is 3927C. With the exception of the synthetic nihonium all of the elements of the boron group have stable isotopes. 234 gcm 3 Color.
The atoms of this group.
The elements of the periodic table sorted by melting point. Notes on the Melting Point of particular elements. 35 E shows even richer features. The chemical elements of the periodic chart sorted by. If the pressure is increased to 10 atmospheres carbon graphite is observed to melt at 3550 C. We say that such a body melts.
 Source: meritnation.com
Source: meritnation.com
Value given for alpha form. The first nuclear reactors which came on-line during this period also made use of boron in their control rods. Below the melting point the solid is the more stable state of the two. They are described by Diophantine relation nn 0 tϕϕ 0 s where n 0 is the number of state per unit. Note that these points are associated with the standard atmospheric pressure.
 Source: britannica.com
Source: britannica.com
Boron is used in pyrotechnics and flares to produce a green color. If the pressure is increased to 10 atmospheres carbon graphite is observed to melt at 3550 C. Metalloids are the elements found along the stair-step line that distinguishes metals from non-metals. Boiling Point Density gcm 3 Boron. Boiling point The temperature at which the liquidgas phase change occurs.
 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
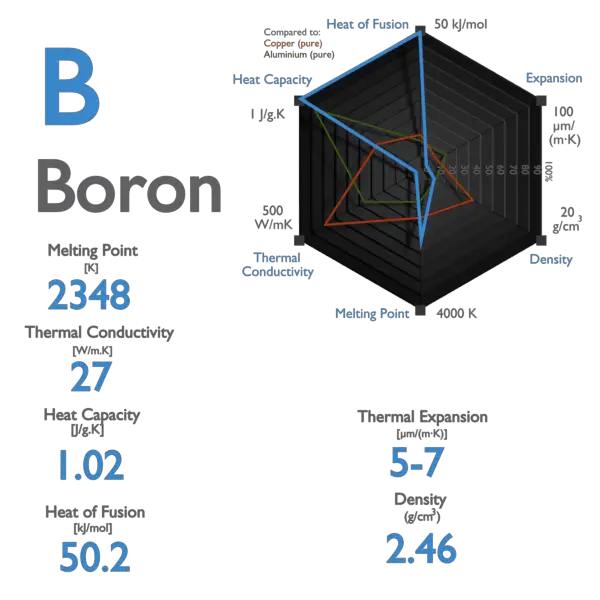
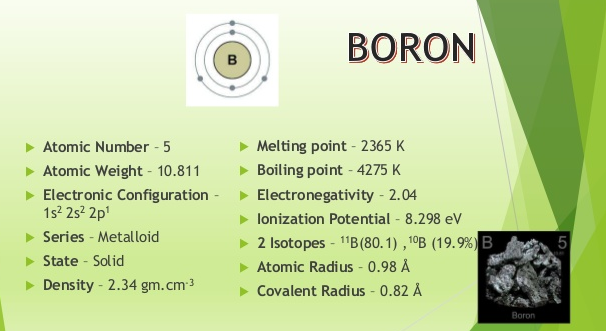
25500 C 282315 K 46220 F Number of ProtonsElectrons. At the melting point the two phases of a substance liquid and vapor have identical free energies and therefore are equally likely to exist. The melting point of boron is 2079C its boilingsublimation point is at 2550C the specific gravity of crystalline boron is 234 the specific gravity of the amorphous form is 237 and its valence is 3. The melting point of iron Fe at the outer liquid core-inner solid core 330 GPa pressures at a depth of 5150 km in the Earth was suggested to provide an absolute temperature limit. Boron Melting Point and Boiling Point.
 Source: rsc.org
Source: rsc.org
Boiling point The temperature at which the liquidgas phase change occurs. Value given for diamond form. Melting point of Boron is 2079C. Note that these points are associated with the standard atmospheric pressure. In the following table the use row is the value recommended for use in other Wikipedia pages in order to maintain consistency across content.
 Source: materials.gelsonluz.com
Source: materials.gelsonluz.com
Crystalline boron is almost inert chemically at ordinary temperatures. Very toxic by inhalation. Boron has interesting optical properties. Boron nitride began to be used in Japanese cosmetics and in 1951 a production method for boron fibers was developed. Hexagonal boron nitride h-BN.
 Source: api.simply.science
Source: api.simply.science
Value given for diamond form. Very toxic by inhalation. Hexagonal boron nitride h-BN. The boiling point of a substance is the temperature at which this phase change boiling or. The melting point of an element is basically the energy required to change the state of an element from its solid state to its liquid state.
 Source:
Source:
The chemical elements of the periodic chart sorted by. At normal atmospheric pressure carbon does not melt when heated it sublimes. The elements of the periodic table sorted by melting point. At normal atmospheric pressure arsenic does not melt when heated. The boiling point of a substance is the temperature at which this phase change boiling or.
 Source: shutterstock.com
Source: shutterstock.com
Very toxic by inhalation. In the following table the use row is the value recommended for use in other Wikipedia pages in order to maintain consistency across content. The melting point is specific for a given substanceFor example the melting point of ice frozen water is 0 C. Boron tribromide appears as a colorless fuming liquid with a pungent odor. The melting point of a substance is the temperature at which it changes state from solid to liquid at atmospheric pressure.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Melting point of Boron is 2079C. At the melting point the two phases of a substance liquid and vapor have identical free energies and therefore are equally likely to exist. 10811 amu Melting Point. The melting point also defines a condition in which the solid and liquid can exist in equilibrium. Consider the nitride for example - just the 2.
 Source: askiitians.com
Source: askiitians.com
It is also a temperature at which a solid crystal turns into a liquid. The elements of the periodic table sorted by melting point. Gallium has very low melting point 303K. Reference Kelvin Celsius Fahrenheit Comments 1 H hydrogen H 2 use. Notes on the Melting Point of particular elements.
If you find this site serviceableness, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title melting point of boron by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.