Melting point of argon
Home » datasheet » Melting point of argonMelting point of argon
Melting Point Of Argon. 86 - Elements in earthcrust-39. At normal atmospheric pressure carbon does not melt when heated it sublimes. When heated carbon undergoes a phase change directly from solid to gas. Why different elements and compounds have different melting and boiling points.

54 - Year of discovery-101. Value given for monoclinic beta form. The melting point of a substance is the temperature at which it changes state from solid to liquid at atmospheric pressure. Iron is a group 6 and period 4 metal. The melting point also defines a condition in which the solid and liquid can exist in equilibrium. Not applicable EVAPORATION RATE Butyl Acetate1.
Follow the link below to get values for the listed properties of argon at varying pressure and temperature.
Gas not applicable FLAMMABILITY. Argon is a chemical element with the symbol Ar and atomic number 18. Alloy add-ons also suppress the melting range lower. 35 - Covalenz radius. Property Argon Appearance colorless Odor none Physical state gas pH NA Vapor Pressure NA Vapor Density 178 gL Boiling point -1224 deg. At normal atmospheric pressure arsenic does not melt when heated.
 Source: chemicool.com
Source: chemicool.com
It is also a temperature at which a solid crystal turns into a liquid. 87 - Ionization energy. These topics are covered in various places elsewhere. Argon isotope of mass 40. Not applicable EVAPORATION RATE Butyl Acetate1.
 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
Pure iron Fe has a fixed melting point of 1535 C chromium Cr of 1890 C and nickel Ni of 1453 C compared to 1400-1450 C for stainless steel of type 304. For liquids it is known as the freezing point and for solids it is called the melting point. The most abundant isotope of argon in the universe is argon-36 which is made when stars with a mass about 11 times greater than the Sun are in their silicon-burning phase. Melting point of Argon is -1892C. Reference Kelvin Celsius Fahrenheit Comments 1 H hydrogen H 2 use.
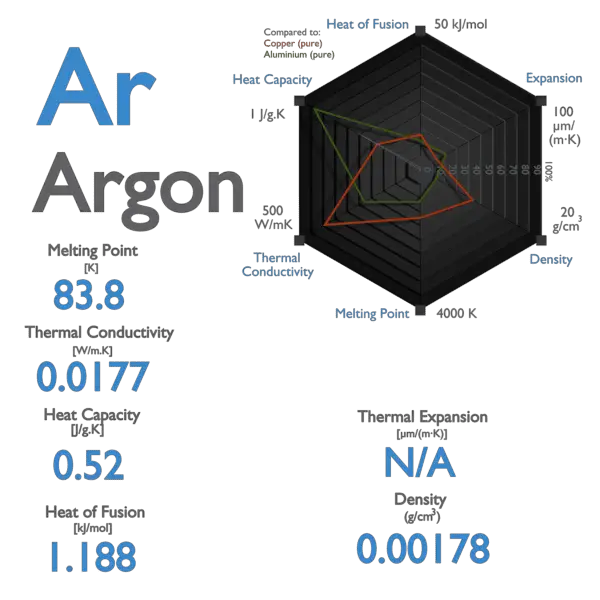 Source:
Source:
The graph shows how melting points and boiling points vary across period 3. Density at STP 1784 gL. 36 - Vanderwaals radius-112. Let us look at the elements in the ascending order of their melting points. Melting point The temperature at which the solidliquid phase change occurs.
 Source: material-properties.org
Source: material-properties.org
Argon is isolated on a large scale by the fractional distillation of liquid air. We say that such a body melts. Melting point The temperature at which the solidliquid phase change occurs. In general boiling is a phase change of a substance from the liquid to the gas phase. SAFETY DATA SHEET GHS product identifier Other means of identification Product type Section 1.
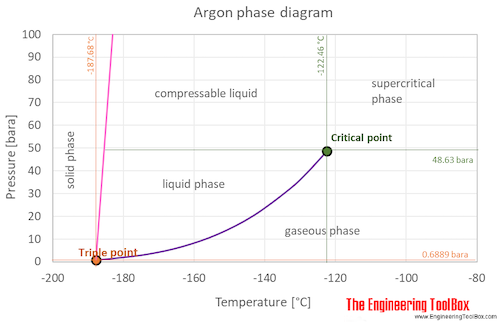 Source: engineeringtoolbox.com
Source: engineeringtoolbox.com
There are many reasons to effect for melting and boiling points of elements and compounds. At the melting point the solid and liquid phases exist in equilibrium. In the following table the use row is the value recommended for use in other Wikipedia pages in order to maintain consistency across content. 273 K 0 C Strictly speaking it should be 27315 rather than 273 but the less precise value is acceptable at A Level. Value given for alpha form.
 Source: britannica.com
Source: britannica.com
Below the melting point the solid is the more stable state of the two. The following table shows the common argon properties including melting point boiling point specific gravity and density of argon. Argon is isolated on a large scale by the fractional distillation of liquid air. Argon Product use SyntheticAnalytical chemistry. 80 - Elements in human body-7.
 Source: rsc.org
Source: rsc.org
We say that such a body melts. Not applicable EVAPORATION RATE Butyl Acetate1. Thus it melts at high temperatures ie 801C whereas ice is a compound comprising of hydrogen bonds whose strength is less than ionic bonds. The graph shows how melting points and boiling points vary across period 3. There are many reasons to effect for melting and boiling points of elements and compounds.
 Source: chemistry.stackexchange.com
Source: chemistry.stackexchange.com
Argon Melting Point and Boiling Point. At normal atmospheric pressure carbon does not melt when heated it sublimes. 246048 C 411 F density 1 atm 0 C 089990 glitre. Argon is isolated on a large scale by the fractional distillation of liquid air. Argon Product use SyntheticAnalytical chemistry.
 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
Argon is isolated on a large scale by the fractional distillation of liquid air. C K 273 eg. When heated carbon undergoes a phase change directly from solid to gas. Argon isotope of mass 40. We say that such a body melts.

Not applicable EVAPORATION RATE Butyl Acetate1. It is also a temperature at which a solid crystal turns into a liquid. SAFETY DATA SHEET GHS product identifier Other means of identification Product type Section 1. Density and specific weight. Learn More in these related Britannica articles.
If you find this site convienient, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title melting point of argon by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.