Melting point magnesium
Home » datasheet » Melting point magnesiumMelting point magnesium
Melting Point Magnesium. At the melting point of a metal it is in equilibrium between its solid and liquid phases. Click on any elements name for further chemical properties environmental data or health effects. 2 - Atomic number-259. 1850 Melting Point Notes.
 Properties Of Pure And Alloyed Magnesium At Its Melting Point 94 Download Table From researchgate.net
Properties Of Pure And Alloyed Magnesium At Its Melting Point 94 Download Table From researchgate.net
Value given for diamond form. A substances melting point depends on pressure and is usually specified at standard pressure in reference materials. For liquids it is known as the freezing point and for solids it is called the melting point. Value given for alpha form. 11070 C 138015 K 20246 F Number of ProtonsElectrons. Whether you are processing the metal or using metal components in a high-temperature setting.
Magnesium is a famous example.
The charge on the nuclei increases. In theory the melting point of a solid is the same as the freezing point of the liquid the point at which it turns into a solid. We say that such a body melts. The charge on the nuclei increases. Up to date curated data provided by Mathematicas ElementData. This list contains the 118 elements of chemistry.
 Source: material-properties.org
Source: material-properties.org
The terms melting point or freezing point are often interchanged depending on whether a substance is being heated or cooled. Value given for hexagonal gray form. If the pressure is increased to 10 atmospheres carbon graphite is observed to melt at 3550 C. All ionic compounds have high melting points for this reason. For example the melting point of ice frozen water is 0 C.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
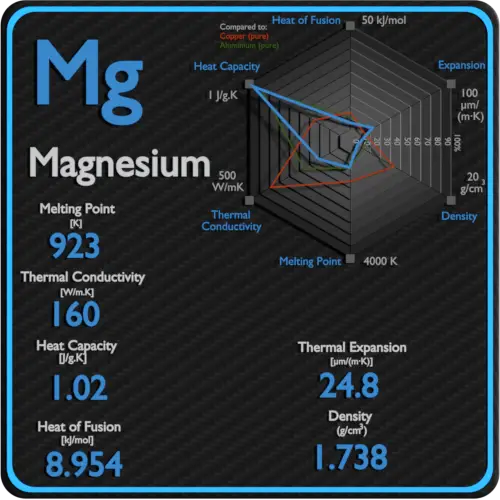
The melting point of a substance depends on pressure and is usually specified at a standard pressure such as 1 atmosphere or 100 kPa. The thermal and electrical conductivity of magnesium and its melting point are very similar to those of aluminum. In theory the melting point of a solid is the same as the freezing point of the liquid the point at which it turns into a solid. Melting point is the temperature at which a solid turns into a liquid. 6500 C 92315 K 12020 F Boiling Point.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
This requires more heat energy to overcome. The number of delocalised electrons increases. 1738 gcm 3 Color. At the melting point the solid and liquid phases exist in equilibrium. The charge on the nuclei increases.
 Source: chemguide.co.uk
Source: chemguide.co.uk
1738 gcm 3 Color. 1850 Melting Point Notes. Sodium chloride has a high melting point because of the strong electrostatic attraction between its positive and negative ions. At normal temperatures it is stable in air and. At the melting point the two phases of a substance liquid and vapor have identical free energies and therefore are equally likely to exist.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
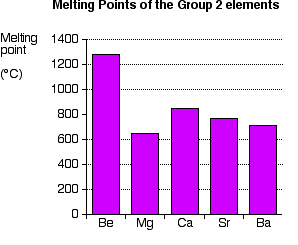
These salts are typical ionic halides being highly soluble in waterThe hydrated magnesium chloride can be extracted from brine or sea waterIn North America magnesium chloride is produced primarily from Great. Melting points of hydrocarbons alcohols and acids - Melting temperature C and F with varying carbon number up to C33. The melting point is the highest temperature at which crystallization may occur. Sodium magnesium and aluminium are all metals. Alkaline Earth Crystal Structure.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Adding a heat will convert the solid into a liquid with no temperature change. The melting point of a solid and the freezing point of the liquid are normally the same. Value given for yellow phosphorus form. Metals - Boiling Temperatures - Metals and their boiling. Water freezes at the same temperature and turns into ice.
 Source: onyxmet.com
Source: onyxmet.com
Hexagonal Density 293 K. The melting point is specific for a given substance. At normal atmospheric pressure carbon does not melt when heated it sublimes. One of the most important characteristics of a metal is its melting point also known as its melting temperature. The melting point or rarely liquefaction point of a solid is the temperature at which a sustance changes state from solid to liquid at atmospheric pressure.
 Source: chemistry.stackexchange.com
Source: chemistry.stackexchange.com
The melting point is also referred to as liquefaction point solidus or liquidus. This list contains the 118 elements of chemistry. The elements of the periodic table sorted by melting point. 11070 C 138015 K 20246 F Number of ProtonsElectrons. Hexagonal Density 293 K.
 Source: chemistry.stackexchange.com
Source: chemistry.stackexchange.com
6500 C 92315 K 12020 F Boiling Point. The terms melting point or freezing point are often interchanged depending on whether a substance is being heated or cooled. Like heavily oxidizing materials flammable metals would require a vacuum or non-oxygen environment when processing. Density g cm 3 Density is the mass of a substance that would fill 1 cm 3 at room temperature. 1738 gcm 3 Color.

Magnesium chloride is the name for the chemical compound with the formula MgCl 2 and its various hydrates MgCl 2 H 2 O xAnhydrous MgCl 2 contains 255 elemental magnesium by mass. For example the melting point of ice frozen water is 0 C. When heated carbon undergoes a phase change directly from solid to gas. Metal Alloys - Specific Heats - Specific heat of metal alloys like brass bronze and more. Helium does not solidify at standard pressure.
If you find this site helpful, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title melting point magnesium by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.