Boiling point xylene
Home » datasheet » Boiling point xyleneBoiling point xylene
Boiling Point Xylene. Corrosion - Corrosion in piping systems - caused by thermodynamic and electrochemical processes - corrosion problems and methods of protection and prevention. 5 gL 20 C Solubility in diethyl ether. Class IIIA Flash Point equal to or greater than 140F but less than 200F Class IIIB Flash Point equal to or greater than 200F Notice that boiling point is only used to. NFPA 704 fire diamond 1.
 Xylene Wikipedia From en.wikipedia.org
Xylene Wikipedia From en.wikipedia.org
It is solid at room temperature and begins to melt above approximately 37 C 99 F and its boiling point is above 370 C 698 F. 573 K not precisely defined Boiling point. Toxic T GHS pictograms. Paraffin wax or petroleum wax is a soft colorless solid derived from petroleum coal or oil shale that consists of a mixture of hydrocarbon molecules containing between twenty and forty carbon atoms. LD 50 median. Decomposes Solubility in water.
Corrosion - Corrosion in piping systems - caused by thermodynamic and electrochemical processes - corrosion problems and methods of protection and prevention.
Corrosion - Corrosion in piping systems - caused by thermodynamic and electrochemical processes - corrosion problems and methods of protection and prevention. Common applications for paraffin wax include lubrication. Lethal dose or concentration LD LC. Each point on this line therefore describes the vapor. The solid line connecting points B and C in this phase diagram contains the combinations of temperature and pressure at which the pure solvent and its vapor are in equilibrium. Class IIIA Flash Point equal to or greater than 140F but less than 200F Class IIIB Flash Point equal to or greater than 200F Notice that boiling point is only used to.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Corrosion - Corrosion in piping systems - caused by thermodynamic and electrochemical processes - corrosion problems and methods of protection and prevention. 5 gL 20 C Solubility in diethyl ether. At or above 73F and below 100F. Chemical Resistance of Rubbers and Elastomers - Rsistance to chemicals. Common applications for paraffin wax include lubrication.
Source: researchgate.net
Some fuels and their boiling points at atmospheric pressure. Toxic T GHS pictograms. Paraffin wax or petroleum wax is a soft colorless solid derived from petroleum coal or oil shale that consists of a mixture of hydrocarbon molecules containing between twenty and forty carbon atoms. Common applications for paraffin wax include lubrication. At or above 73F and below 100F.
 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
LD 50 median. The boiling point is defined as the temperature at which the saturated vapor pressure of a liquid is equal to the surrounding atmospheric pressure. Corrosion - Corrosion in piping systems - caused by thermodynamic and electrochemical processes - corrosion problems and methods of protection and prevention. Melting point 300 C 572 F. Decomposes Solubility in water.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
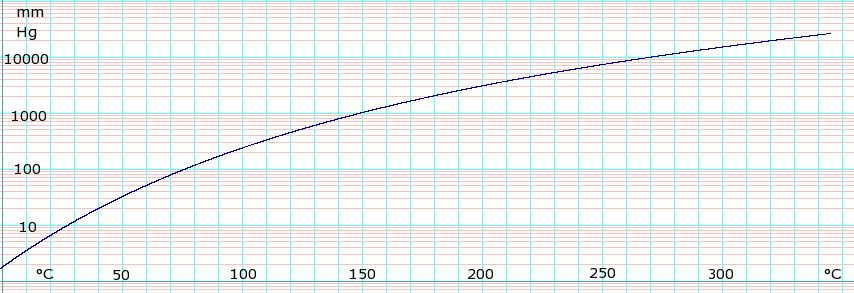
The solid line connecting points B and C in this phase diagram contains the combinations of temperature and pressure at which the pure solvent and its vapor are in equilibrium. 5 gL 20 C Solubility in diethyl ether. Material Properties - Material properties for gases fluids and solids - densities specific heats viscosities and more. Chemical Resistance of Rubbers and Elastomers - Rsistance to chemicals. The figure below shows the consequences of the fact that solutes lower the vapor pressure of a solvent.
Source: chemspider.com
It is solid at room temperature and begins to melt above approximately 37 C 99 F and its boiling point is above 370 C 698 F. Paraffin wax or petroleum wax is a soft colorless solid derived from petroleum coal or oil shale that consists of a mixture of hydrocarbon molecules containing between twenty and forty carbon atoms. 12-Dimethylbenzene ortho-Xylene o-Xylol Colorless liquid with an aromatic odor. The boiling point of a substance is the temperature at which it can change state from a liquid to a gas throughout the bulk of the liquid. Corrosion - Corrosion in piping systems - caused by thermodynamic and electrochemical processes - corrosion problems and methods of protection and prevention.
 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
Lethal dose or concentration LD LC. Decomposes Solubility in water. Chemical Resistance of Rubbers and Elastomers - Rsistance to chemicals. Common applications for paraffin wax include lubrication. At or above 73F and below 100F.
 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
The figure below shows the consequences of the fact that solutes lower the vapor pressure of a solvent. Class IIIA Flash Point equal to or greater than 140F but less than 200F Class IIIB Flash Point equal to or greater than 200F Notice that boiling point is only used to. Corrosion - Corrosion in piping systems - caused by thermodynamic and electrochemical processes - corrosion problems and methods of protection and prevention. Some fuels and their boiling points at atmospheric pressure. 12-Dimethylbenzene ortho-Xylene o-Xylol Colorless liquid with an aromatic odor.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
5 gL 20 C Solubility in diethyl ether. Common applications for paraffin wax include lubrication. 573 K not precisely defined Boiling point. Each point on this line therefore describes the vapor. The boiling point is defined as the temperature at which the saturated vapor pressure of a liquid is equal to the surrounding atmospheric pressure.
 Source: chemsynthesis.com
Source: chemsynthesis.com
Paraffin wax or petroleum wax is a soft colorless solid derived from petroleum coal or oil shale that consists of a mixture of hydrocarbon molecules containing between twenty and forty carbon atoms. Lethal dose or concentration LD LC. The solid line connecting points B and C in this phase diagram contains the combinations of temperature and pressure at which the pure solvent and its vapor are in equilibrium. The figure below shows the consequences of the fact that solutes lower the vapor pressure of a solvent. The boiling point of a substance is the temperature at which it can change state from a liquid to a gas throughout the bulk of the liquid.
 Source: kiaexport.com
Source: kiaexport.com
The figure below shows the consequences of the fact that solutes lower the vapor pressure of a solvent. Each point on this line therefore describes the vapor. It is solid at room temperature and begins to melt above approximately 37 C 99 F and its boiling point is above 370 C 698 F. Chemical Resistance of Rubbers and Elastomers - Rsistance to chemicals. The solid line connecting points B and C in this phase diagram contains the combinations of temperature and pressure at which the pure solvent and its vapor are in equilibrium.
If you find this site value, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title boiling point xylene by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.