Benzene melting point
Home » datasheet » Benzene melting pointBenzene melting point
Benzene Melting Point. Most pure organic compounds melt over a narrow temperature range of 1-2 C. Nitrobenzene is an organic compound with the chemical formula C 6 H 5 NO 2It is a water-insoluble pale yellow oil with an almond-like odorIt freezes to give greenish-yellow crystals. It is a colourless liquid and has an aromatic odour. In general trans alkenes have a higher melting point.
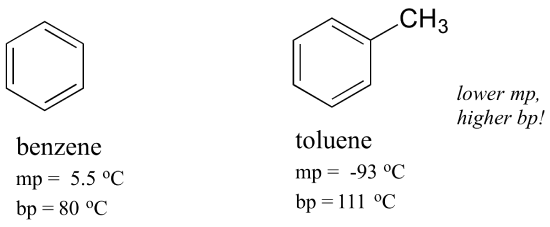 3 3 Melting Points And Boiling Points Introductory Organic Chemistry From openoregon.pressbooks.pub
3 3 Melting Points And Boiling Points Introductory Organic Chemistry From openoregon.pressbooks.pub
Most pure organic compounds melt over a narrow temperature range of 1-2 C. At the critical point there is no change of state when pressure is increased or if heat is added. 55C Benzene shows resonance. It is lighter than water. In contrast the cis isomer is a polar molecule with a higher boiling point 60 o C vs 48 o C because of the net. A demonstration of bromine substitution and addition reactions is helpful at this point and a virtual demonstration may be initiated by.
In this process Benzene sulphonic acid is exposed to superheated steam leading to the formation of benzene.
At the critical point there is no change of state when pressure is increased or if heat is added. It has a density of 087g cm-3. It also shows the saturation pressure with changes in temperature. At the melting point the solid and liquid phases exist in equilibrium. Benzene is a natural constituent of crude oil and is one of the elementary petrochemicals. C 6 H 5-SO 3 H H 2 O C 6 H 6 H 2 SO 4.
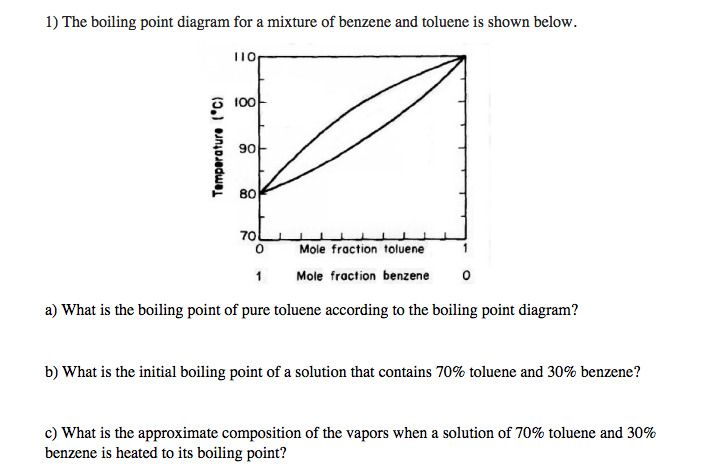 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
The chemical reactivity of benzene contrasts with that of the alkenes in that substitution reactions occur in preference to addition reactions as illustrated in the following diagram some comparable reactions of cyclohexene are shown in the green box. It is a colourless liquid and has an aromatic odour. More detailed definitions and examples of molecular structures of the different classes of organic compounds are given below the figures. Benzene is an organic chemical compound with the molecular formula C 6 H 6The benzene molecule is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar ring with one hydrogen atom attached to each. Melting point is a characteristic property of solid crystalline substances.
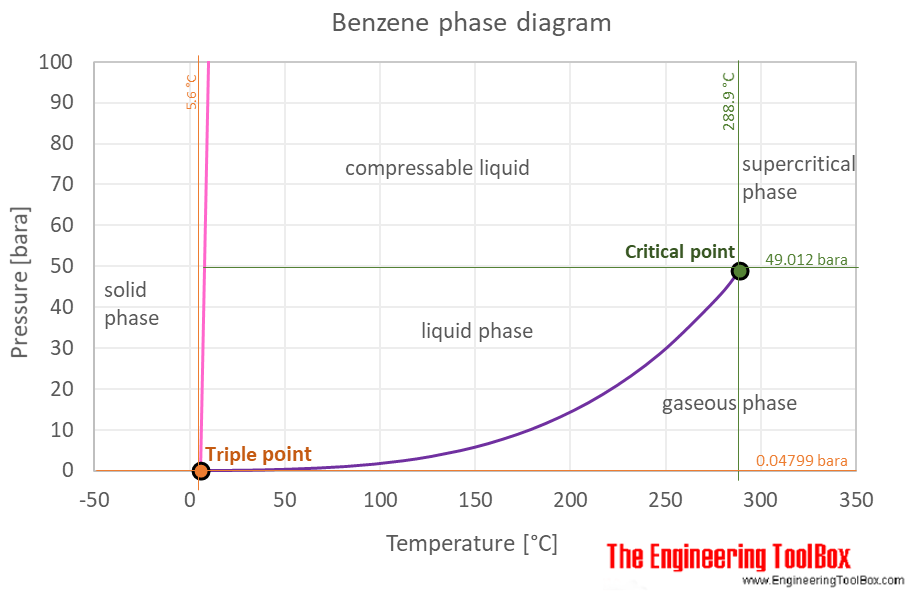 Source: engineeringtoolbox.com
Source: engineeringtoolbox.com
It is produced on a large scale from benzene as a precursor to anilineIn the laboratory it is occasionally used as a solvent especially for electrophilic reagents. At the melting point the solid and liquid phases exist in equilibrium. It has a density of 087g cm-3. These were some basic methods for the laboratory preparation of benzene. Benzene can be prepared from sulphonic acids through their hydrolysis.
 Source: openoregon.pressbooks.pub
Source: openoregon.pressbooks.pub
Nitrobenzene is an organic compound with the chemical formula C 6 H 5 NO 2It is a water-insoluble pale yellow oil with an almond-like odorIt freezes to give greenish-yellow crystals. Most pure organic compounds melt over a narrow temperature range of 1-2 C. Benzene is a natural constituent of crude oil and is one of the elementary petrochemicals. It is the temperature at which the solid phase changes to the liquid phase. Benzene can be prepared from sulphonic acids through their hydrolysis.

C 6 H 5-SO 3 H H 2 O C 6 H 6 H 2 SO 4. To learn about other processes for the commercial and laboratory preparation of benzene download. For example despite being nonpolar the trans isomer of 12-dichloroethane has a higher melting point 50 o C than the cis isomer 80 o C because of higher symmetry which allows for compact packing in the solid phase. In this process Benzene sulphonic acid is exposed to superheated steam leading to the formation of benzene. Benzene can be prepared from sulphonic acids through their hydrolysis.
 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
The triple point of a substance is the temperature and pressure at which the three phases gas liquid and solid. More detailed definitions and examples of molecular structures of the different classes of organic compounds are given below the figures. The melting point of a substance is the temperature at which it changes state from solid to liquid at atmospheric pressure. In general trans alkenes have a higher melting point. The presence of a soluble impurity almost always causes a decrease in the melting point expected for the pure compound and a broadening of the.
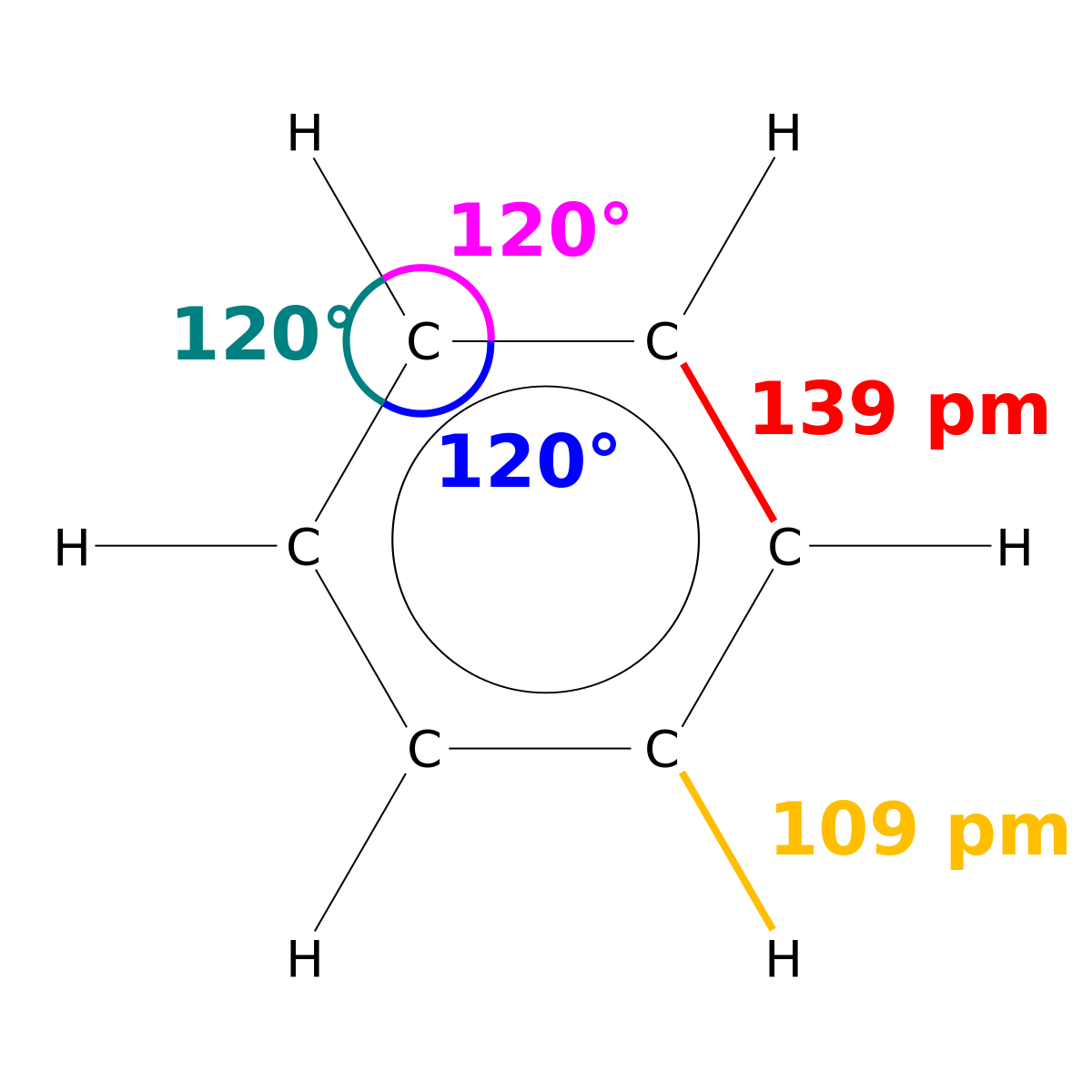 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
It has a density of 087g cm-3. For example despite being nonpolar the trans isomer of 12-dichloroethane has a higher melting point 50 o C than the cis isomer 80 o C because of higher symmetry which allows for compact packing in the solid phase. Most pure organic compounds melt over a narrow temperature range of 1-2 C. In general trans alkenes have a higher melting point. The melting point range is defined as the span of temperature from the point at which the crystals first begin to liquefy to the point at which the entire sample is liquid.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
55C Benzene shows resonance. At the melting point the solid and liquid phases exist in equilibrium. A demonstration of bromine substitution and addition reactions is helpful at this point and a virtual demonstration may be initiated by. These were some basic methods for the laboratory preparation of benzene. Benzene is immiscible in water but soluble in organic solvents.

55C Benzene shows resonance. Benzene has a moderate boiling point and a high melting point. Melting point - the temperature at which a solid turns into a liquid. It is lighter than water. It has a density of 087g cm-3.
 Source: ddbst.com
Source: ddbst.com
To learn about other processes for the commercial and laboratory preparation of benzene download. These were some basic methods for the laboratory preparation of benzene. A substances melting point depends on pressure and is usually specified at standard pressure in reference materials. Melting point - the temperature at which a solid turns into a liquid. In general trans alkenes have a higher melting point.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
At the melting point the solid and liquid phases exist in equilibrium. The presence of a soluble impurity almost always causes a decrease in the melting point expected for the pure compound and a broadening of the. Benzene can be prepared from sulphonic acids through their hydrolysis. The melting point range is defined as the span of temperature from the point at which the crystals first begin to liquefy to the point at which the entire sample is liquid. The curve between the critical point and the triple point shows the benzene boiling point with changes in pressure.
If you find this site convienient, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title benzene melting point by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.